تأثیرات زیست محیطی مصالح ساختمانی
انجام مقاله عمران
تأثیرات زیست محیطی مصالح ساختمانی
چکیده
نگرانی های رو به رشدی درباره اثرات زیست محیطی ساختمانها منجر به درخواستهای بیشتری برای ساختمانهای سازگار با محیط زیست و مصالح ساختمانی شده است.
پیش از این مطالعات کلی که نمایانگر کلیت تأثیرات زیست محیطی مصالح ساختمانی و اجزای خدمات ساختمانی برای ساختمانها باشد، انجام نشده است.
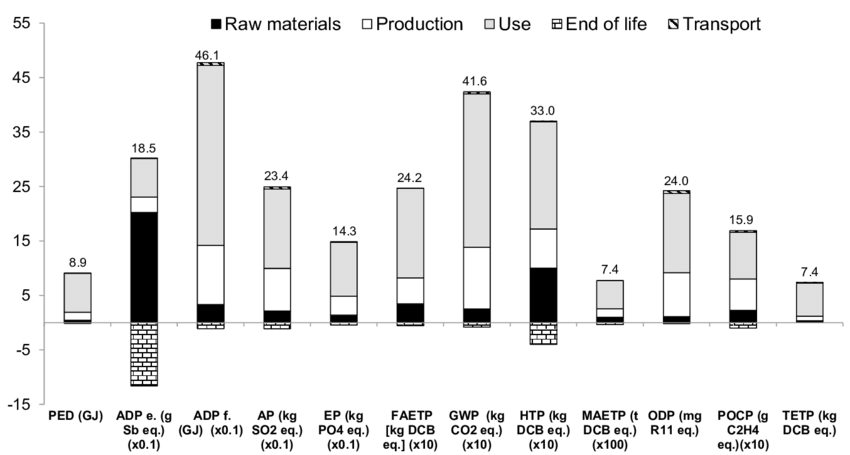
این مقاله برآن است تا با گزارش نقشه های زیست محیطی چرخه عمر کلی ساختمان ها، همچنین رتبه بندی سفارشات اثرات زیست محیطی کلیه مصالح ساختمانی و مواد و قطعات خدمات ساختماني برای ساختمانهاي تجاري این شکاف را پر کند.

انجام پایان نامه عمران
بیست و پنج ساختمان تجاری در هنگ کنگ مشتمل بر سه ساختمان اداری درجه A ، چهار ساختمان اداری درجه B ، یک ساختمان اداری درجه یک C ، چهار مرکز خرده فروشی و سه هتل ، برای مطالعه ما انتخاب شده است.
بر اساس این نمونه های جمع آوری شده، اختلاف آماری در اثرات زیست محیطی چرخه عمر متوسط برای انواع ساختمان های متفاوت علی رغم برخی تغییرات جزئی شناخته شده، یافت نشد.
متعاقباً ، 10 نوع مصالح ساختمانی و 10 نوع مؤلفه خدمات ساختمانی برای تأثیرات زیست محیطی قابل توجه چرخه عمر بر ساختمانهای تجاری شناسایی شده اند.
از میان همه موارد بتن، نوار تقویت کننده، کابلهای برق مسی و باس بارهای مسی به عنوان چهار ماده مهم یا مؤلفه های تأثیرات زیست محیطی در کل چرخه عمر طبقه بندی شدند.
این موارد بایستی اهداف اصلی برای بهبود عملکرد زیست محیطی ساختمانهای تجاری را تشکیل دهد.
بحث و نتیجه گیری
این مطالعه یکی از ابتدایی ترین و جامع ترین مطالعاتی است که بطور موفقیت آمیزی نقشه هایی که باعث ایجاد اثرات زیست محیطی چرخه عمر می شود را نشان می دهد.
یک موضوع تأثیر چرخه عمر کامپوزیت در ابتدا برای هر نوع ماده و مصالح ساختمانی و پس از آن برای هر ساختمان مورد بررسی بدست آمده است.
رویکرد پیشنهادی دو مزیت مهم را ارائه می دهد.
این مساله در ابتدا یک رویکرد عینی را برای رتبه بندی ساختمان و مواد و مصالح خدمات ساختمانی مورد استفاده در ساختمان های تجاری با جمع کردن تأثیرات زیست محیطی متنوع چندگانه آنها در یک نقطه تأثیر چرخه عمر واحد فراهم می کند.
سپس ارزیابی های زیست محیطی ساده شده را برای طرح های مختلف یک ساختمان تجاری با استفاده از داده های فهرست چرخه عمر وزنی که بایستی برای مواد و مصالح ساختمانی انجام شود، را ممکن می سازد.
بر اساس نمونه های جمع آوری شده ما، اثرات زیست محیطی متوسط چرخه عمر با وجود برخی تغییرات جزئی، اختلاف آماری خاصی میان پنج نوع ساختمان مختلف را نشان نداد.
پس می توان نتیجه گرفت که برای تجزیه و تحلیل تأثیرات زیست محیطی کلی، نیازی به تفکیک پنج نوع ساختمانهای تجاری مختلف نیست.
مصالح و اجزا، از جمله مبلمان داخلی، که طی یک طول عمر 50 ساله نیاز به جایگزین شدن دارند، 33٪ از کل تأثیرات زیست محیطی را تشکیل می دهند.
بنابراین، از دیدگاه زیست محیطی، انتخاب مصالح و مؤلفه های جایگزین در مرحله ساخت به همان اندازه انتخاب مواد و اجزای سازنده در مرحله طراحی اهمیت دارد.
همچنین، مشاهده گردید که سهم درصد یک ماده یا مؤلفه یا حتی یک سیستم به نقطه LCI کل با درصد سهم آن به کل وزن ساختمان در نسبت مستقیم تفاوتی ندارد.
ممکن است یک مصالح ساختمانی که سهم چندانی در کل وزن ساختمان دارد، سهم قابل توجهی در کل امتیازات LCI و بالعکس نداشته باشد.
برای مثال، اجزای خدمات ساختمانی اگرچه از نظر وزن کمتر از 2٪ وزن کلی را به خود اختصاص داده اند اما بطور تقریبی 27٪ از تأثیرات چرخه عمر کلی یک ساختمان تجاری را به خود اختصاص داده اند.
در مقابل، بتن که بیش از 74٪ از کل وزن ساختمان را به خود اختصاص داده، تنها حدود 14٪ از کل تأثیر چرخه عمر را به خود اختصاص داده است.
ده مورد از مصالح ساختمانی و اجزای خدمات ساختمانی به دلیل اثرات چشمگیر زیست محیطی چرخه عمر بر ساختمانهای تجاری شناسایی شده اند.
بتن ، نوار تقویت کننده، گچ، گچ کاری و سیمان کاری، به دلیل سنگین ترین وزن به ترتیب در رتبه اول تا پنجم سهم داشتن در کل اثرات زیست محیطی چرخه عمر در یک ساختمان تجاری قرار گرفتند.
با توجه به این موضوع ، طراحان ساختمان و سازندگان محصول باید برای بهبود عملکرد کلی محیط زیست برای ساختمانها ، تأکید بیشتری بر روی این مواد و مؤلفه ها کنند.

از طرف دیگر، جایگزینی مواد شناسایی شده با مواردی که اثرات زیست محیطی کمتری دارند حتی اگر در همه موارد قابل اعمال نباشد، ممکن است به کاهش تأثیرات زیست محیطی کل آنها در ساختمانها کمک کند.
علی رغم همه این گفته ها اگر یافته های این مطالعه با تأثیر کلی بر اثرات زیست محیطی در یک عنصر و نه در قالب نوعی ماده ارائه شود، با ارزش تر خواهد بود.
بنابراین ، یافته هایی که در قالب عنصر شوند، مطمئناً باید طراحان ساختمان را در ارزیابی اثرات زیست محیطی چرخه عمر گزینه های طراحی شان تسهیل کند.
برای مشاهده مطالب بیشتر به سایت www.farzdon.ir مراجعه نماید.
تأثیرات زیست محیطی مصالح ساختمانی
انجام پروپوزال عمران
Abstract
The growing concerns over the environmental impacts of buildings have led to increasing demands for more environmental friendly buildings and building materials.
Hitherto, there are not any comprehensive studies that show the overall environmental impact profiles of building materials and building services components for buildings.
This paper intends to bridge this gap by reporting overall lifecycle environmental profiles of buildings as well as the ranking orders of environmental impacts of all the building materials and building services materials and components for commercial buildings.
Twenty-five commercial buildings in Hong Kong, which include three Grade A office buildings, four Grade B office buildings, one Grade C office buildings, four retail centers and three hotels, have been selected for our study.
Based upon these collected samples, no statistical differences were found in the average lifecycle environmental impacts for different building types despite some minor variations were detected.
Subsequently, 10 types of building materials and 10 types of building services components have been identified for their significant lifecycle environmental impacts on commercial buildings.
Among all, concrete, reinforcement bar, copper power cables, and copper bus bars were ranked to be the four most significant materials or components to the total lifecycle environmental impacts. These should form the major targets for improvements in environmental performance of commercial buildings.
Discussions and conclusions
This study represents one of pioneering and the most comprehensive studies that successfully revealed the lifecycle environmental impact profiles of building materials and building services components for five different types of high-rise commercial buildings in Hong Kong.
A composite lifecycle impact point has initially been derived for each type of material and component, and subsequently for each examined building. The proposed approach offers two major advantages.
First, it provides an objective approach for ranking the building and building services materials and components used in commercial buildings by aggregating their multiple diverse environmental impacts into a single lifecycle impact point.
Second, it enables simplified environmental assessments to be performed for different designs of a commercial building by using the weighted lifecycle inventory data for building materials and components.
Based upon our collected samples, the average lifecycle environmental impacts were found to have no statistical differences among five different building types despite some minor variations were detected.
Thus, it can be concluded that it is not necessary to distinguish among five different types of commercial buildings for the analysis of the total environmental impacts.
Materials and components, such as interior furnishings, that needed to be replaced within a 50 year lifespan accounted up to 33% of total environmental impacts.
Thus, from the environmental perspective, selection of replacement materials and components during occupation stage is as important as selection of materials and components during design stage.
Also, it was observed that the percentage contribution of a material or component, or even a system to the total LCI point does not vary in direct proportion with its percentage contribution to the total building weight.
A building material that has a significant contribution to the total building weight may not have a significant contribution to the total LCI points, and vice versa.
For instance, building services components accounted for approximately 27% of total lifecycle impacts for a commercial building although they only accounted for less than 2% in terms of total weight.
In contrast, concrete that contributed for more than 74% of the total building weight only accounted for approximately 14% of total lifecycle impact points.
Ten building materials and 10 building services components have been identified for their significant lifecycle environmental impacts on commercial buildings. Concrete, reinforcement bar, and plaster, render and screed, ranked the first, second and fifth, respectively, in their overall contributions to the total lifecycle environmental impacts due to their heaviest weight contents in a commercial building.
In view of this, building designers and product manufacturers should place more emphasis on these materials and components for improving the overall environmental performance for buildings.
Alternatively, substitution of the identified materials with the ones that incur smaller environmental impacts may also help reduce their total environmental impacts on buildings even though it may not be practical in all cases.
Nonetheless, the findings of this study would be more valuable if the overall environmental impacts had been presented in an elemental rather than in a material format.
Thus, findings that are presented in elemental format should certainly facilitate the building designers in evaluating the lifecycle environmental impacts of their design alternatives